How To Calculate Labor Cost, Rate, & Percentage?

Following are the formulas you can use to calculate accurate labor cost, rate, and percentage.
| Calculate Labor Cost 💰 |
| Total Labor Cost = Gross Wages + Payroll Taxes + Benefits Costs + Overhead Expenses |
| Calculate Labor Cost Percentage 📊 |
| Labor Cost Percentage = (Total Labor Cost / Total Revenue) × 100 |
| Calculate Labor Rate ⏱️ |
| Labor Rate = Total Labor Costs / Total Labor Hours |
Knowing how to calculate labor costs is important for managing finances and making decisions for businesses and employees.
Knowing the process behind calculating these labor costs, rates, and percentages helps set competitive prices for products or services, ensuring the company stays profitable. It also helps decide on how many people to hire and how to manage them.
The top three benefits of accurate labor cost calculation are:
- Planning Money: Calculating employee costs helps plan how to spend money, making sure resources are used well.
- Pricing Products or Services: Considering employee costs when setting prices helps keep profit margins steady.
- Evaluating Performance: Figuring out employee costs helps find areas where work could be better and helps make smart choices about hiring and resources.
Try Buddy Punch For Free
| What is Labor Cost? |
| Labor cost is the total amount a business spends on paying its employees over a certain time period, like a week or a month. It includes all types of pay, such as hourly wages, salaries, bonuses, and benefits such as health insurance and paid time off. |
How To Calculate Labor Cost?

Following are the ways to calculate labor cost.
1. Gather Necessary Data
To calculate labor costs accurately, gather all the necessary information.
This includes,
- how much you pay your employees,
- the taxes you have to pay on their wages,
- the cost of their benefits like health insurance,
- and any other costs related to their work.
⚠️ Note: Other costs could be bonuses or extra payments.
2. Calculate Gross Pay
To calculate gross wages, you need to know the employee’s hourly rate and the number of hours worked.
Multiply the hourly rate by the number of hours worked to get the gross wages.
Here’s the total gross wages labor cost formula:
| Gross Wages = Hourly Rate × Number of Hours Worked |
3. Add Payroll Taxes
Payroll taxes are deductions from employees’ wages for things like Social Security, Medicare, and state and federal unemployment taxes.
To find the total payroll taxes, multiply each rate by the employee’s total pay.
The formula for calculating total payroll taxes is as follows:
| Total Payroll Taxes = (Social Security Rate + Medicare Rate + State Unemployment Tax Rate + Federal Unemployment Tax Rate) * Employee’s Total Pay |
Where:
- Social Security Rate: The percentage rate set by law for Social Security tax.
- Medicare Rate: The percentage rate set by law for Medicare tax.
- State Unemployment Tax Rate: The percentage rate set by the state for unemployment tax.
- Federal Unemployment Tax Rate: The percentage rate set by the federal government for unemployment tax.
- Employee’s Total Pay: The total wages or salary earned by the employee before any deductions.
4. Incorporate Benefits Costs
Including benefits costs means adding up the cost of things like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off that the employer provides to each employee.
To do this, calculate the total cost of each benefit per employee for a specific time period.
The formula for calculating the total cost of benefits per employee can be expressed as follows:
| Total Cost of Benefits Per Employee = (Cost of Health Insurance + Cost of Retirement Plans + Cost of Paid Time Off) / Number of Employees |
Where:
- Cost of Health Insurance: The total amount spent on providing health insurance coverage for all employees.
- Cost of Retirement Plans: The total amount spent on providing retirement benefits for all employees.
- Cost of Paid Time Off: The total amount spent on providing paid time off benefits for all employees.
- Number of Employees: The total number of employees within the organization.
5. Account for Overhead Expenses
Overhead expenses are costs like rent, utilities, and office supplies that support the workforce but aren’t tied to individual employees.
To figure out these costs, add up all the overhead expenses for a certain time period.
Divide the total overhead costs by the total number of employees to find the overhead cost per employee.
The formula for calculating overhead cost per employee is:
| Overhead Cost per Employee = Total Overhead Expenses / Total Number of Employees |
Where:
- Total Overhead Expenses: The sum of all overhead expenses for a certain time period.
- Total Number of Employees: The total count of employees in the organization.
6. Calculate the Total Labor Cost
To calculate how much you spend on labor for a certain time, add up all the different parts.
- Add the gross wages, which is the total pay for all employees.
- Add the payroll taxes, which are the taxes the employer pays for the employees.
- Include the benefits costs, like health insurance and retirement contributions.
- And then overhead expenses, which are costs like rent and utilities, are added.
Labor Cost Formula
The labor cost calculation formula involves adding together various components to determine the total labor cost for a specified period.
The formula can be summarized as follows:
| Total Labor Cost = Gross Wages + Payroll Taxes + Benefits Costs + Overhead Expenses |
How Can We Use The Labor Cost Formula To Calculate Annual Labor Cost & Monthly Labor Costs?
To calculate annual labor costs using the labor cost formula, multiply the number of labor hours worked annually by the labor rate per hour.
The formula would be as follows,
| Annual Labor Cost = Total Labor Hours Worked Annually × Labor Rate per Hour. |
Similarly, to find monthly labor costs, divide the annual labor cost by 12 (number of months).
The formula would be as follows,
| Monthly Labor Cost = Annual Labor Cost / 12 |
Ready to give Buddy Punch a try?
For free trial, no credit card required.
How To Calculate Labor Rate?

Calculating the labor rate involves determining the cost of labor per hour for each employee.
There are two ways to calculate the labor rate:
1. Incremental Labor Rate
The incremental labor rate is how much extra it costs a business for each additional worker hired.
To find this rate, divide the change in total labor cost by the change in the number of workers.
The formula for calculating the incremental labor rate is:
| Incremental Labor Rate = Change in Number of Workers / Change in Total Labor Cost |
2. Fully Loaded Labor Rate
To find the fully loaded labor rate, add up all the costs of having an employee for a certain time.
This includes wages, taxes, and benefits. Then, divide this total cost by the number of work hours the employee works.
The formula to find the fully loaded labor rate is:
| Fully Loaded Labor Rate = (Total Cost of Employee) / (Number of Hours Worked) |
Labor Rate Calculation Formula
To find out how much each employee costs, divide their share of the total labor cost by the total hours they worked.
This formula helps businesses see how much they’re spending on each employee per hour.
| Labor Rate = Total Labor Costs / Total Labor Hours |
We already know how to calculate the total labor cost from the previous section discussion. Let’s learn how to calculate “Total Labor Hours.”
How To Calculate Total Labor Hours?
Calculating total labor hours accurately is crucial for various purposes, such as scheduling, payroll processing, and tracking employee productivity.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you calculate total labor hours accurately:
- Collect Information: Get the number of hours each employee worked during the period you’re interested in, like a week, month, or year.
- Add Regular Hours: Count up the normal hours each employee worked. These are usually the hours they agreed to work in their contracts.
- Check Overtime: If employees worked more than their regular hours, note down those extra hours. Overtime hours are usually paid at a higher rate.
- Calculate Total Hours: Add together the regular hours and any overtime hours for each employee to find out their total hours worked.
- Find the Overall Total: Add up all the hours worked by all employees to know the total labor hours for that period.
The formula for calculating total labor hours can be summarized as follows:
| Total Labor Hours = Σ (Regular Hours Worked + Overtime Hours Worked) |
Where:
- Σ denotes the sum or total.
- Regular Hours Worked are the standard hours agreed upon in each employee’s contract.
- Overtime Hours Worked are any hours worked beyond the regular hours, typically compensated at a higher rate.
Ready to start a free trial?
No credit card required, all features included.
How To Calculate Labor Cost Percentage?

To calculate the labor cost percentage, divide the total labor cost by the total revenue for a specific period and multiply by 100.
The formula is:
| Labor Cost Percentage = (Total Labor Cost / Total Revenue) × 100 |
What is Standard Vs. Actual Labor Cost?
| Aspect | Standard Labor Cost | Actual Labor Cost |
| Definition | The expected or planned labor cost based on predicted rates or estimates. | The real cost of labor incurred during a specific period, including wages, benefits, and related expenses. |
| Calculation | Figured out using standard rates or estimates for wages, benefits, and other labor-related expenses. | Determined by actual wages paid, benefits provided, and other labor-related expenses incurred. |
| Variability | Generally stays the same unless there are changes in labor rates or policies. | Can vary based on factors like actual hours worked, overtime, and changes in benefits. |
| Purpose | Used for budgeting, forecasting, and setting labor cost goals. | Used for evaluating performance against budgeted targets, spotting cost differences, and adjusting future budgets. |
| Importance | Aids in financial planning and setting practical labor cost targets. | Helps in understanding actual labor cost performance and improving cost control strategies. |
What is The Importance of Calculating Labor Cost Accurately?

Accurate labor cost calculations are important for businesses to manage their finances well and make good decisions.
They help with budgeting by showing exactly how much is spent on wages, benefits, and other labor costs.
1. Impact on Profitability
The impact on profitability refers to how much money a business makes after accounting for costs like labor.
When labor costs are calculated accurately, a business can set prices that cover expenses and make a profit.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting is about setting goals for how to use money and figuring out how much to spend on different things.
Forecasting uses past data and trends to guess what might happen in the future financially. It helps predict problems or good opportunities ahead of time.
3. Setting Competitive Prices
Setting competitive prices involves choosing prices for your products or services that are appealing to customers compared to what other businesses are charging.
You want to find a balance where the price is enough to cover your costs and make a profit, but not too high that customers go somewhere cheaper.
4. Evaluating Employee Productivity
Evaluating employee productivity involves checking how well your employees are doing their jobs and how effectively they’re managing their time.
This includes looking at things like how much work they’re getting done, if they’re meeting deadlines, and how well they’re working with others.
Direct Cost Vs. Indirect Labor Cost

Here’s the difference between direct costs and indirect labor costs.
1. Direct Labor Cost
Direct labor cost, also known as direct labor rate, direct labor hours, or hourly labor cost, encompasses the wages, benefits, and taxes paid to employees directly involved in the production process or service delivery.
It’s the cost that directly contributes to the creation of goods or services and can be easily attributed to specific items or projects based on the total number of hours worked.
2. Indirect Labor Cost
Indirect labor costs include expenses related to employees who are not directly engaged in production or service provision, such as administrative staff, HR personnel, accountants, and maintenance workers.
Indirect labor costs may also involve training costs, fixed costs, and other overhead expenses not directly tied to production but essential for business operations.
Can Labor Costs Vary by Industry?
Yes, labor costs can vary between different types of businesses.
Industries that need workers with specialized skills or knowledge, like technology or healthcare, often have higher labor costs.
Where a business is located can also affect labor costs, with urban areas generally having higher wages than rural areas.
But, does the labor cost formula change with industry type?
Well, it does not.
Consider the following labor cost example.
How To Calculate Restaurant Labor Cost Percentage?

It’s important for restaurant managers to figure out how much they’re spending on staff compared to their overall costs.
Restaurant labor cost percentage in the restaurant industry refers to the portion of a restaurant’s total revenue that is allocated to paying employee wages and related expenses.
It is calculated by dividing the total labor costs (including wages, benefits, payroll taxes, and any other labor-related expenses) by the total revenue generated by the restaurant, and then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
The formula for calculating restaurant labor cost percentage is:
| Labor Cost Percentage = (Total Labor Costs / Total Revenue) × 100 |
Labor costs typically include wages for kitchen staff, servers, bartenders, hosts/hostesses, as well as management salaries and benefits.
So, as you can see, the formula for calculating restaurant labor cost percentage is the same as discussed above, i.e., the formula is universal, only labor rates vary.
How Does Employee Scheduling Software Help in Calculating Accurate Restaurant Labor Costs?
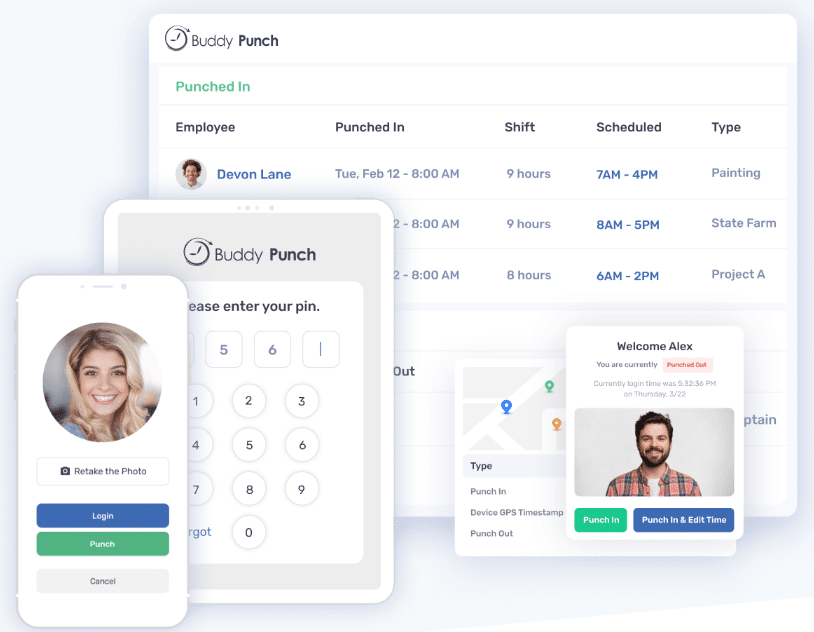
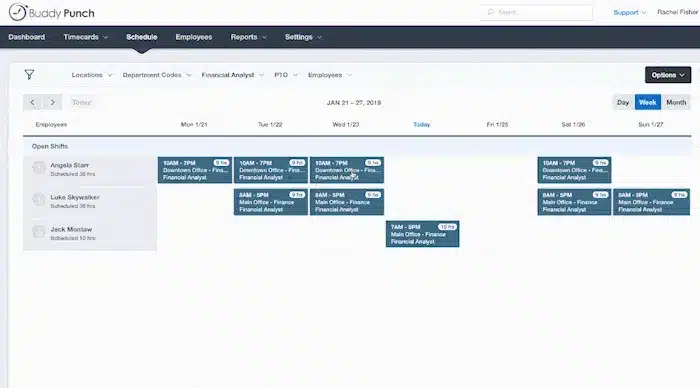
Employee scheduling software helps restaurant owners (especially in the fine dining niche) manage staff shifts and employee labor costs accurately. It helps owners make smart decisions about staffing levels based on expected business, preventing overstaffing during slow times and understaffing during busy periods.
The software also allows quick adjustments to schedules when demand changes.
This software connects with other important parts of restaurant management, like inventory and sales systems (like POS systems & COGS systems). It helps owners track key indicators like cost of goods sold, total sales, food costs, average labor cost, and prime cost, so they can find ways to make more amount of money.
Additionally, scheduling software helps with keeping employees happy by handling vacation days, sick days, employee benefits, incentives, and rewards.
The bottom line is this, using time tracking and scheduling software like Buddy Punch creates a better workplace. You can lower the number of employee turnover and save money on additional costs such as onboarding/hiring and training new staff.
Ready to give Buddy Punch a try?
For free trial, no credit card required.
How To Calculate Total Operating Costs Metric?
Total operating cost refers to the sum of all expenses incurred by a business in its day-to-day operations, including both fixed and variable costs.
These costs typically include expenses such as wages, rent, utilities, raw materials, and maintenance.
To calculate total operating costs, you add up all expenses associated with running the business during a specific period, regardless of whether they fluctuate with production levels or remain constant.
Here’s the formula for calculating total operation costs,
| Total Operating Costs = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs |
How To Calculate Variable Costs?
Variable costs are expenses that vary in direct proportion to the level of production or sales. Examples include raw materials, direct labor, and sales commissions.
To calculate total variable costs, you multiply the variable cost per unit by the number of units produced or sold during a given period.
Here’s the formula for calculating total variable cost,
| Total Variable Costs = Variable Cost per Unit × Number of Units Produced or Sold |
Tips To Optimize Labor Costs
Optimizing labor costs means carefully planning and taking action to improve how efficiently your team works while keeping costs in check.
1. Implement Workforce Management Software

Implementing workforce management software can greatly improve how a business handles its workforce and can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency gains.
The software helps schedule, track employee attendance, assign tasks, and monitor performance.
2. Invest To Develop and Train Employees

Investing in training and developing employees is essential for improving business performance and controlling labor costs.
Training helps employees become more skilled and efficient, leading to better quality work. It also keeps them up-to-date with industry trends and technology.
3. Regularly Review and Adjust Labor Budgets
Regularly reviewing labor budgets helps businesses ensure they match current needs and goals.
Staying proactive and flexible with labor budgets helps businesses adapt to market changes and keep labor costs in line with financial goals.
4. Consider Automating Tasks to Minimize Labor Expenses
Automating repetitive tasks helps businesses save money and work more efficiently.
Automation can be used in many areas like entering data, making schedules, managing inventory, and helping customers.
This not only cuts labor costs but also makes work more accurate and productive.
Factors Affecting Labor Cost Calculation
Following are the different types of factors that can affect labor cost calculations.
1. Industry Type
Different industries have different labor costs.
Industries needing more specialized skills, like technology or healthcare, tend to have higher labor costs.
In contrast, industries like retail or hospitality, which require fewer skills, usually have lower labor costs.
2. Geographic Location
Geographic location refers to where a business is situated, which can impact its labor costs.
Wages and living expenses vary across regions and countries, with urban areas generally having higher labor costs due to higher living expenses.
3. Employee Skill Level
Employees with higher skills usually earn more because of their specialized knowledge and expertise.
Industries that need highly skilled workers, like technology or healthcare, usually have higher labor costs than those with simpler jobs.
4. Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements, like minimum wage laws and overtime pay rules, vary by region and industry.
These rules affect how businesses calculate labor costs and ensure they follow the law.
How Does Labor Cost Impact Pricing Strategies?
Labor cost directly affects how businesses set prices. It’s a big part of the total cost and influences decisions on pricing.
If labor costs are high, prices might be higher than competitors with lower labor costs. This can change how a business is seen in the market and by customers.
Managing labor well is important because it can help lower costs and keep prices competitive.
How is Labor Cost Calculation Related To Employee Turnover?

Calculating how much it costs to pay workers is closely connected to how often they leave their jobs. When lots of employees leave, it can really hurt a business’s profits.
When turnover rates are high, it costs more to deal with workers leaving because the business has to spend money on finding, hiring, and training new employees.
Also, when there’s a lot of turnover, it messes up the schedule and makes it harder for full-time and hourly workers to do their jobs. This makes things less efficient and can lead to extra costs like paying for overtime or hiring temporary workers to keep things running smoothly.
Small business owners need to keep a close eye on how much time employees are spending at work.
High turnover can also mean more employees calling in sick or filing for workers’ compensation, which adds even more costs for the business.
Plus, when people keep leaving, it can make the rest of the employees feel unhappy and less motivated to do their jobs well. That means they might not work as hard, which just makes the turnover problem worse.
So, it’s super important for businesses to find ways to keep employee retention high to save money and make sure everything runs smoothly.