What is Overtime and How To Calculate Overtime Percentage?

Overtime refers to the additional hours an employee works beyond their regular working hours.
Typically, standard working hours are defined by an employer and are often set at 40 hours per week.
When an employee works more than these standard hours, the additional hours are considered overtime.
Overtime work is usually compensated at a higher rate than the regular hourly wage.
The increased pay is meant to provide extra compensation for employees who work longer hours, recognizing the additional time and effort they contribute to the job.
Accurately calculating overtime has become increasingly vital for both employers and employees.
As we navigate calculating overtime percentage, it’s imperative to recognize its significance in evaluating productivity and resource allocation.
For employees, comprehending overtime and its implications is essential for managing work-life balance and understanding how their efforts translate into compensation.
Software solutions emerge as invaluable tools in this context, addressing several challenges associated with overtime calculations.
Top three issues when calculating overtime percentages are,
Precision in Overtime Calculations
Overtime calculations can be complex, especially when dealing with various types such as non-guaranteed, voluntary, tipped, time off in lieu (TOIL), and eight-and-eighty overtime.
Time tracking software solutions excel in handling these intricacies, ensuring precise calculations and reducing the likelihood of errors.
By automating the process, these tools account for different scenarios, enabling accurate compensation for employees based on the specific nature of their overtime work.
Streamlined Payroll Processing
Traditional overtime calculation methods often involve manual data entry, increasing the chances of errors and leading to inefficiencies in the payroll process.
Overtime calculation software streamlines this operation by automating calculations and integrating seamlessly with existing payroll systems.
This saves time and enhances accuracy, eliminating the need for extensive manual checks.
The result is a more efficient and error-free payroll processing system that benefits employers and employees.
Adherence to Labor Laws and Regulations
Overtime calculation software is designed to stay up-to-date with the latest labour laws and regulations, automatically incorporating any changes into its calculations.
By providing accurate and compliant overtime calculations, the software contributes to a fair and transparent working environment, fostering trust between employers and employees.
Try Buddy Punch For Free
What Is Overtime and How Does This Work?
Overtime refers to any hours an employee works beyond their regular schedule.
Overtime hours typically exceed standard working hours and vary based on factors like customs, trade practices, legislation, or agreements between employers and workers.
The purpose of overtime regulations is to discourage excessive work hours, ensuring employee well-being and overall economic productivity.
Local jurisdictions determine overtime eligibility, and most workers, regardless of their employment status (full-time, part-time, temporary, or casual), qualify if they surpass a set amount of working time.
Regulations vary globally; each country, state, or region may have distinct policies.
For instance, in the U.S., the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) governs overtime requirements, distinguishing between exempt and non-exempt employees.
| What Is Employee Overtime Percentage? |
| Employee Overtime Percentage is the percentage of overtime hours worked in comparison to the standard working hours of a company. As explored in a comprehensive guide by ExcelDataPro, this metric goes beyond numerical representation; it offers valuable insights for HR (Human Resources) professionals to strategize recruitment needs and assess workforce productivity and performance. Understanding and managing employee overtime percentage is essential for optimizing productivity and curbing unnecessary costs associated with increased turnover rates and recruitment expenses. |
Who Qualifies For Overtime Pay?
The following are the ways used to check who qualifies for overtime pay.
1. Full-Time Employees
Full-time employment typically implies a standard 40-hour workweek, and any hours worked beyond this threshold may qualify for overtime compensation.

Employment laws such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) often influence eligibility determination.
In the context of the FLSA, full-time employees who exceed 40 hours per week are entitled to overtime pay.
This additional compensation, typically one and a half times the regular hourly wage, financially acknowledges the extra effort and time invested beyond the standard work hours.
It’s crucial for employers to accurately classify employees as full-time and diligently track their work hours to ensure compliance with overtime regulations.
Likewise, employees should be aware of their rights regarding overtime pay, advocating for fair compensation when their workload exceeds the standard expectations.
2. Temporary Employees
Temporary employees are individuals hired for a specific duration or task, often to meet seasonal demands or short-term projects.
Overtime qualification for temporary employees hinges on various factors, including employment status and the applicable labour laws.
Temporary employees can qualify for overtime pay if their work hours surpass the standard threshold set by labour regulations.
Like their full-time counterparts, temporary employees are typically entitled to overtime compensation at a rate higher than their regular hourly wage when they exceed the stipulated standard work hours.
Employers must accurately classify temporary employees and diligently monitor their work hours to ensure compliance with overtime regulations.
3. Part-Time Employees
Part-time employees are individuals who work fewer hours than their full-time counterparts, often due to personal preferences or scheduling constraints.
However, part-time employees may still qualify for overtime pay under specific circumstances.
The eligibility of part-time employees for overtime is typically determined by the total number of hours worked in a given workweek.
If part-time employees exceed the standard workweek hours defined by labour laws, they become eligible for overtime compensation.
This means that, despite their reduced weekly schedule, part-time workers are entitled to additional pay at a rate higher than their regular hourly wage when their hours extend beyond the prescribed limit.
Is Overtime Calculated By Day Or Week?
The calculation of overtime can vary depending on the country, industry, and specific labor laws in place.

In many countries, including the United States, overtime is typically calculated on a weekly basis.
This means that any hours worked beyond a certain threshold within a given week, usually 40 hours, are considered overtime and eligible for additional pay.
However, it’s important to note that this may vary, so it is always best to consult the labor laws and regulations specific to your location or place of employment.
What Are The Different Types Of Overtime Pay Percentage?
Following are the different types of overtime percentage.
1. Tipped Overtime
Tipped overtime is a type of overtime calculation that is particularly relevant in the hospitality and food services industries.
For employees falling under the tipped category, it’s crucial to understand the nuanced calculations involved.
Tipped overtime typically means factoring in the base hourly wage and the additional income from tips.
2. Compulsory Overtime
Compulsory overtime situations can arise in various industries, such as healthcare, emergency services, or manufacturing, where unexpected events or high demand necessitate a workforce’s immediate and mandatory extension.
Employees engaged in compulsory overtime often face situations where refusal to work beyond regular hours is not an option due to the critical nature of the work or contractual obligations.
Calculating compulsory overtime pay involves considering factors like the base hourly wage and any applicable premium rates for overtime hours.
Employers must adhere to labour laws and employment contracts to ensure proper compensation for employees subjected to compulsory overtime.
3. Voluntary Overtime
Voluntary overtime is when employees willingly choose to work beyond their regular schedule.
This type of overtime is typically undertaken to seize opportunities for increased earnings or contribute to projects requiring additional effort.
Voluntary overtime often comes with varying rates.
Some employers may offer a premium pay rate for voluntary hours beyond the standard workweek, while others may stick to the average hourly wage.
The terms and conditions surrounding voluntary overtime are typically outlined in employment contracts, collective bargaining agreements, or company policies.
One critical aspect of voluntary overtime is the mutual agreement between employers and employees.
Both parties must be transparent and communicate effectively about expectations, compensation, and the voluntary nature of the extra hours.
4. Eight-And-Eighty Overtime
Eight-and-eighty overtime pay structure involves a distinct breakdown in compensation, where employees receive a premium for working extended hours.
This model incentivises employees to take on additional hours beyond the standard workweek.
Employers may choose the “Eight-And-Eighty” approach to acknowledge the increased effort and commitment required for extended work hours.
When calculating overtime percentages under the eight-and-eighty overtime model, it is essential to consider both components separately.
The first eight hours contribute to the total overtime at the standard premium rate, while the subsequent hours carry a higher premium.
5. Time Off In Lieu (Toil)
Time off in lieu (TOIL) allows employees to accrue extra time worked as paid time off in the future.
Under TOIL, employees who work beyond their regular hours accumulate extra hours that can be utilized as additional paid time off instead of receiving overtime pay.
Employers and employees often agree on TOIL arrangements, fostering a collaborative approach to managing workload fluctuations.
Clear communication and written agreements ensure both parties understand the terms and conditions associated with Time Off In Lieu, contributing to a harmonious work environment.
6. Non-Guaranteed Overtime
Unlike guaranteed overtime, which is pre-scheduled or assured, non-guaranteed overtime occurs unpredictably and is often based on operational needs.
Employees engaged in non-guaranteed overtime may work additional hours beyond their regular schedule when the demand arises, such as during busy seasons or unexpected work surges.
This type of overtime introduces variability, making it challenging for employees to anticipate when they might be required to work beyond their standard hours.
Employers typically communicate non-guaranteed overtime expectations as needed, and employees may have the flexibility to accept or decline such opportunities based on their availability and personal commitments.
Ready to give Buddy Punch a try?
For free trial, no credit card required.
Why Are Some Employees Exempt From Working Extra Hours?
Certain employees are exempt from working extra hours due to the nature of their roles and responsibilities.
These exemptions are typically granted to individuals who perform management functions primarily or hold substantial control over their work hours while earning at least two times the average industrial wage.
Job titles alone do not determine exemption; instead, they hinge on factors such as the level of authority an employee wields within the organization and the nature of their work functions.
Buddy Punch | Best Overtime Tracking App
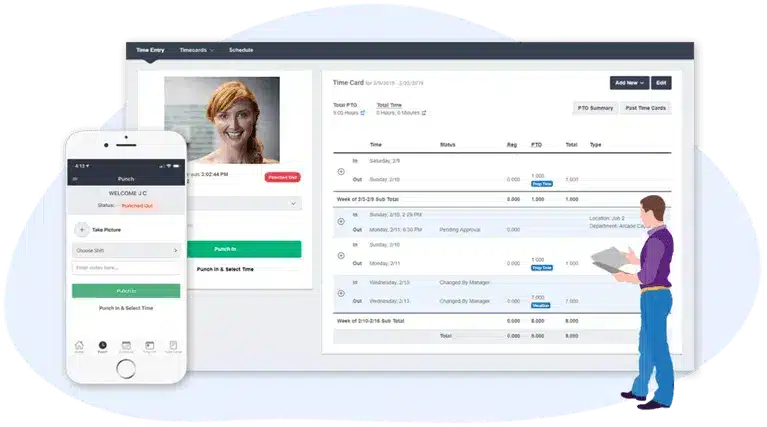
In various industries, from construction to medical, schools, office staff, and SMBs, businesses of all sizes rely on Buddy Punch to revolutionize overtime pay calculations.
This innovative solution ensures accurate tracking of work hours, enhancing precision in overtime calculations.
With seamless integration into payroll systems, Buddy Punch eliminates the hassle of manual computations, saving time and reducing errors.
Unlike traditional methods, Buddy Punch offers a more efficient and reliable approach to overtime pay.
Its user-friendly interface allows employees to clock in and out effortlessly while employers gain real-time insights into attendance.
This not only ensures compliance with labour regulations but also boosts operational efficiency.
By automating overtime calculations, businesses can mitigate errors, improve payroll accuracy, and focus on strategic priorities, making Buddy Punch a superior choice for modern workforce management.
1. Flexible Overtime Calculations
Buddy Punch is a reliable solution that ensures accurate time tracking for worked hours in a workday.
Under this feature, users benefit from a diverse range of overtime types to calculate overtime pay precisely.
Notably, Buddy Punch supports different overtime categories on an individual employee basis, providing flexibility tailored to unique work structures.
2. Auto Calculation
Regarding efficient time management and precise payroll integration, Buddy Punch stands out with its auto-calculation feature.
This advanced functionality ensures accurate tracking by automatically calculating regular hours, overtime, and double overtime.
With Buddy Punch, there’s no need for manual computations, reducing the risk of errors and streamlining the payroll process.
Businesses can confidently rely on the system to effortlessly determine different pay rates based on the hours worked, guaranteeing that every billable hour is accounted for.
3. Easy Reporting
Incorporating Buddy Punch’s time tracking system provides an easy and efficient way to manage overtime and double overtime.
With this feature, users can effortlessly access detailed reports into overtime and dual overtime hours employees work.

This streamlined process enhances payroll management, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Notably, the payroll export report is a widely used reporting feature, offering a comprehensive Excel view of employees’ hours, overtime, locations, and departments.
By utilizing these reporting features, businesses can maintain precise records, optimize payroll processes, and seamlessly integrate payroll hours, contributing to enhanced productivity and accuracy.
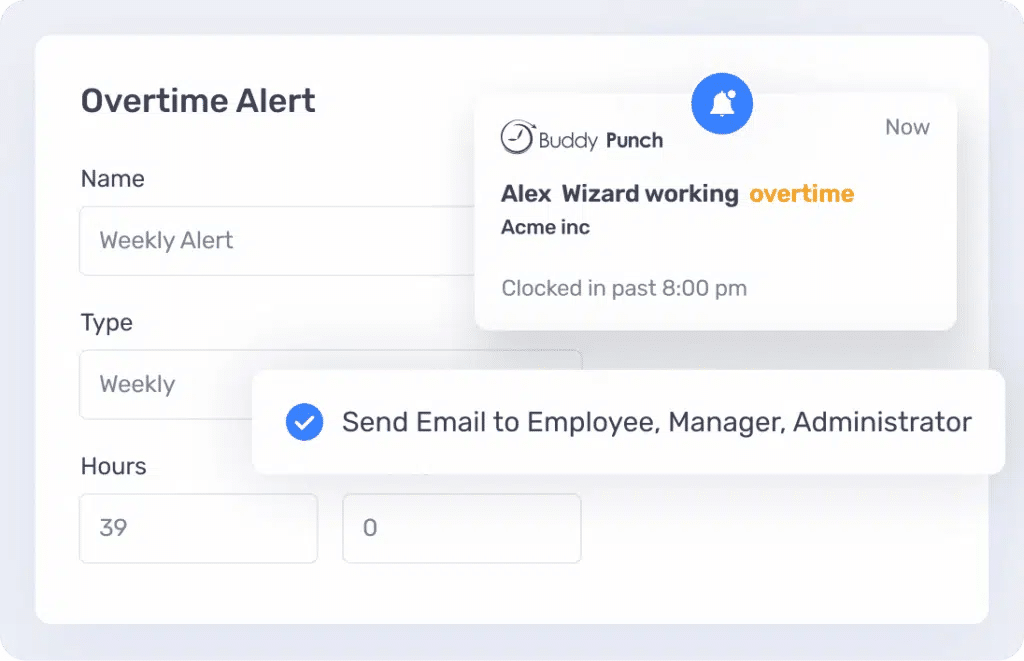
4. Overtime Alerts
Buddy Punch proactively notifies users when an employee approaches or reaches predefined overtime thresholds.
By receiving timely overtime alerts, employers can effectively manage labour costs, prevent unauthorized overtime, and maintain compliance with labour regulations.
The overtime alerts feature provides real-time insights into employee work hours, allowing for swift decision-making and strategic planning.
Buddy Punch’s Online Reviews

“Delighted! As a trucking company and having resources starting their shifts at different times and in different locations it was “effort” in tying this all together to ensure everyone was being paid for correct times – doing payroll was a chore in calling and requesting and then finally imposing deadlines or you don’t get paid which pushes other things back in processing payroll… Week one of deployment -> all those issues disappeared!!! Well done Buddy Punch!!!!”
Click here to read the full review.
“Buddy Punch has been my main source for time tracking since I started my new position. It is user friendly!”
Click here to read the full review.
“The ease of clocking in and out, where ever I may need to punch in. I like that employees are able to make an adjustment to their time and then it gets approved by manager. Which is much easier than having to make punches and delete punches.”
Click here to read the full review.
Try Buddy Punch for Free
Ready to start a free trial?
No credit card required, all features included.
If you feel that Buddy Punch might fit your business, sign up for a 14-day free trial (no credit card needed). You can also book a one-on-one demo or view a pre-recorded demo video.
Things To Know Before Calculating Overtime Pay
The following are the things to know before calculating overtime pay.
1. Overtime Laws and Regulations
Each jurisdiction may have specific overtime rules, including eligibility criteria, hourly thresholds, and applicable rates.
Familiarizing yourself with these legal aspects ensures accurate and compliant overtime calculations.
For instance, in the United States, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) stipulates that non-exempt employees must receive overtime pay at least one and a half times their regular hourly wage for hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek.
Similarly, other regions may have their own set of regulations.
By staying informed about these laws, employers can avoid legal pitfalls, foster fair labour practices, and guarantee that overtime pay calculations align with statutory requirements.
2. Define Workweek
As defined by labour laws, a workweek establishes the recurring seven-day period during which an employee’s hours are tracked for overtime eligibility.
It’s vital for employers to clearly define their chosen workweek, which may or may not align with the calendar week.
Once established, this consistent time frame becomes the basis for determining when overtime pay is applicable.
For instance, in the United States, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) typically considers the workweek as any fixed and regularly recurring period of 168 hours — seven consecutive 24-hour periods.
Employers can accurately track and calculate overtime hours by defining the workweek, ensuring compliance with labour regulations and fair compensation practices.
3. Overtime Rate
The overtime rate represents an employee’s additional compensation for working beyond their standard hours, typically exceeding 40 hours per workweek.
As per labour regulations, the overtime rate is often set at one and a half times the regular hourly wage.
This means that the employee is entitled to 1.5 times their usual pay for every hour worked beyond the standard threshold.
For instance, if an employee’s regular hourly wage is $15, the overtime rate would be $22.50 per hour.
4. Exempt vs. Non-Exempt Employees
Exempt and non-exempt classifications hinge on whether employees are subject to or exempt from the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) overtime regulations.
Non-exempt employees are eligible for overtime pay, typically receiving 1.5 times their regular hourly wage for hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek.
On the other hand, exempt employees are exempt from these regulations and do not qualify for overtime pay.
The determination is based on job duties, salary level, and payment structure. Employers must accurately classify their workforce to ensure compliance with labour laws.
5. Record Keeping
When delving into the intricacies of overtime pay, meticulous record-keeping stands out as a crucial aspect.
Employers must maintain accurate and detailed records of employees’ work hours, breaks, and overtime.
Comprehensive record-keeping ensures compliance with labour laws and serves as a safeguard in case of audits or disputes.
Employers should document regular and overtime hours worked, distinguishing between different types of work, and keep these records for a specified period.
6. State Specific Rules
When unravelling the intricacies of overtime pay, understanding state-specific rules is paramount.
Overtime regulations can vary significantly from state to state, influencing factors such as the threshold for overtime eligibility, calculation methods, and any exemptions.
Employers must familiarize themselves with the labour laws specific to their operating state to ensure compliance and fair compensation for employees.
Some states may have more stringent overtime regulations than federal standards, requiring employers to adapt their practices accordingly.
Staying abreast of state-specific rules mitigates legal risks and fosters an environment of transparency and fairness in the employer-employee relationship.
7. Difference Between Salaried Employees and Hourly Employees
Understanding the disparities between salaried and hourly employees is crucial, especially when it comes to aspects like minimum wage, overtime regulations, and legal frameworks enforced by the U.S. Department of Labor.
Delving into the intricacies of federal and state laws, this exploration aims to shed light on critical elements such as regular rate of pay, overtime wages, and working schedules that distinguish these two employment classifications.
Salaried Employees

Annual Salary and Salary Basis
Salaried employees receive a fixed annual salary, providing financial stability and predictability.
They are often exempt from minimum wage and overtime provisions under certain conditions, such as meeting specific duties outlined by federal overtime laws.
Unpaid Overtime and Working Schedule
While salaried employees might not be eligible for overtime pay, they can be required to work beyond the standard 40-hour workweek.
The concept of an “exempt” employee relates to specific criteria, including job duties and salary thresholds.
Outside Sales and Federal Regulations
Salaried employees engaged in outside sales may enjoy exemptions from certain wage and hour regulations, allowing flexibility in their working arrangements.
However, it’s crucial to understand the nuances of federal law to ensure compliance.
Hourly Employees

Hourly Pay and Minimum Wage
Hourly employees receive compensation based on the number of hours worked.
Compliance with federal and state minimum wage laws is imperative, ensuring that workers are fairly compensated for their time and effort.
Overtime Payments and Double Time
Hourly employees are entitled to overtime pay for hours worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek.
The regular rate of pay is a key factor in calculating overtime wages, and in some instances, employees may qualify for double-time pay, particularly when exceeding a specified number of overtime hours.
Wage and Hour Division Compliance
Hourly employees are protected by the wage and hour division, ensuring that they receive proper compensation for their labor.
Employers must adhere to federal and state laws, covering aspects like pay periods and overtime calculations.
Intersection of Both Categories
Regular Wage and Annual Salary Equivalents
Understanding the regular rate of pay for hourly employees is essential for calculating overtime.
This rate may include not only the hourly pay but also additional compensation elements, such as bonuses and commissions. It’s vital for employers to maintain clarity on these factors.
Federal and State Law Harmony
While federal overtime laws set a baseline, state laws may provide additional protections or requirements, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of the legal landscape.
How to Calculate Overtime Percentage?
Following are the ways to calculate overtime percentage.
1. Compute Total Hours
Total hours worked encompass regular and overtime hours logged by an employee within a specified timeframe.
To obtain this figure, sum the standard or contractual hours considered regular and add any additional hours categorized as overtime.
Accurate record-keeping is paramount, ensuring that all hours are meticulously recorded.
Whether using time tracking software, manual timesheets, or other methods, the precision of this data lays the groundwork for precise overtime percentage calculations.
The computed total hours serve as the denominator in the formula, forming the basis for evaluating workforce efficiency, labour costs, and compliance with overtime regulations.
2. Figure Out Your Hourly Rate
Your hourly rate forms the basis for determining overtime pay, and it’s essential to grasp this fundamental element.
To calculate your hourly rate, divide your weekly earnings by the total hours worked in a standard workweek.
This hourly rate is the benchmark for distinguishing between regular and overtime pay rates.
3. Estimate The Overtime Rate
The overtime rate is the multiplier applied to an employee’s regular hourly rate when they surpass the standard weekly working hours.
To estimate the overtime rate, identify the overtime multiplier specified by labour laws or company policies.
Commonly, overtime is compensated at 1.5 times the regular hourly rate for hours worked beyond the standard workweek.
However, certain circumstances may warrant double or more. By estimating the overtime rate, employers and employees gain insight into the additional compensation due for extra hours worked.
4. Multiply the Hourly Rate By the Overtime Pay Rate
While calculating overtime percentage, a critical step involves multiplying the hourly rate by the overtime pay rate.
This computation is fundamental in determining the additional compensation owed for hours worked beyond the standard workweek.
Begin by identifying the regular hourly rate, representing the legal compensation for an hour of work.
Subsequently, ascertain the overtime pay rate, typically 1.5 times the regular rate per labour regulations.
Multiply the hourly rate by the overtime pay rate to reveal the overtime compensation per hour.
How Time Tracking Help When Calculating Overtime Pay?
Time tracking is a powerful ally in this process, offering precise insights into employees’ work hours and activities.
Try Buddy Punch For Free
By leveraging advanced time tracking tools, businesses can effortlessly capture and organize data, ensuring that every minute worked is accurately recorded.
This minimizes the risk of payroll errors and streamlines the calculation of overtime pay by providing a comprehensive overview of regular and extra hours logged by employees.
The integration of time tracking in overtime calculations enhances efficiency, promotes transparency, and establishes a reliable foundation for fair compensation practices, benefiting employers and employees.
What Is The Formula To Calculate Overtime Pay?
The formula to calculate overtime pay depends on the labor laws in your jurisdiction.
In many places, overtime is typically calculated as time and a half (1.5 times) the regular hourly rate for hours worked beyond the standard workweek.
Here’s a general formula:
OvertimePay=(HoursWorkedBeyondStandardWorkweek)×(HourlyRate×1.5)
For example, if the standard workweek is 40 hours, and an employee works 45 hours, with an hourly rate of $15:
Overtime \, Pay = (45 – 40) \times (15 \times 1.5) = 5 \times 22.5 = $112.50
Ensure to check and adhere to the specific overtime regulations in your location, as some jurisdictions might have different rules and rates for overtime calculation.
Strategies To Reduce Overtime Pay Without Compromising Productivity
Following are the strategies to reduce overtime pay without compromising productivity.
1. Implement Smart Scheduling
Implementing intelligent scheduling is crucial to curtail overtime expenses without compromising productivity.
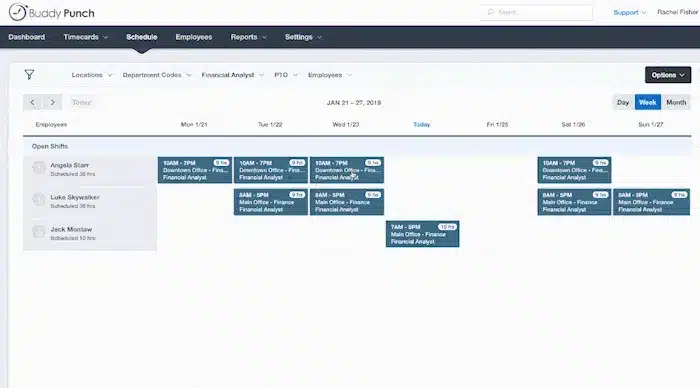
Smart scheduling involves a meticulous approach to aligning staffing levels with fluctuating demand, ensuring optimal coverage during peak periods and preventing unnecessary overtime during lulls.
To implement intelligent scheduling, businesses can leverage predictive analytics and historical data to forecast busy periods, allowing for proactive adjustments to staffing.
Additionally, embracing flexible scheduling options, such as staggered shifts or compressed workweeks, can help distribute workload efficiently.
Moreover, incorporating employee preferences and utilizing scheduling software that automates the process can enhance accuracy and reduce the risk of errors.
2. Set Clear Deadlines
Clear deadlines provide a roadmap for work completion, allowing employees to prioritize tasks efficiently.
This not only aids in preventing last-minute rushes but also contributes to a more organized workflow.
Employers can communicate expectations effectively, enabling teams to allocate their time wisely and avoid unnecessary overtime.
Additionally, leveraging project management tools and software can facilitate transparent communication, aiding in disseminating deadlines and fostering collaboration.
When everyone is on the same page regarding project timelines, it becomes easier to distribute work evenly and avoid the crunch that often leads to extended work hours.
3. Analyze Overtime Trends
Analyzing overtime trends enables employers to pinpoint specific departments, projects, or periods that consistently require additional hours.
This insight is particularly valuable for business owners who seek to optimize their workforce’s efficiency.
By delving into the amount of overtime logged and considering factors like non-discretionary bonuses and shift differentials, eligible employees can be appropriately compensated for their dedication.
This data-driven approach empowers decision-makers to implement proactive measures, such as redistributing workload, adjusting staffing levels, or optimizing project timelines.
For instance, a business owner may identify that certain work schedules or piece-rate compensation structures contribute to increased overtime.
Recognizing these patterns allows for strategic adjustments to avoid unnecessary strain on employees and financial resources.
Moreover, understanding the reasons behind overtime trends allows for introducing preventative measures.
By incorporating considerations like the weekly salary and total pay, employers can develop comprehensive strategies to address the root causes of excessive overtime.
Whether it involves refining workflows, providing additional training, or addressing systemic issues, a proactive response can help mitigate the recurrence of overtime patterns.
In this endeavor, calculating the weighted average of total pay, which includes straight-time pay, total number of overtime hours, and any applicable bonuses, provides a nuanced understanding of compensation dynamics.
Business owners can use this information to fine-tune work schedules, ensuring that employees are compensated fairly while maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
4. Flexible Work Arrangements
Flexible work arrangements empower employees to manage their time better, enhancing overall work-life balance.

This, in turn, can result in increased efficiency during standard working hours and a reduction in the need for overtime.
Employers foster a positive and accommodating work environment by allowing employees to tailor their schedules to better suit personal needs or preferences.
Moreover, flexible work arrangements contribute to employee satisfaction and retention, positively impacting overall productivity.
This strategy addresses the financial aspect of overtime and aligns with modern workplace trends, promoting a healthy work culture.
5. Implement Incentive Programs
Incentive programs can take various forms, such as performance bonuses, recognition awards, or other rewards for achieving specific goals or milestones.

These initiatives inspire employees to enhance their efficiency and foster a sense of accomplishment and job satisfaction.
When employees are motivated by the prospect of earning additional rewards, they are more likely to optimise their work during regular hours, minimizing the need for overtime.
This approach controls labour costs and contributes to a positive work environment.
6. Invest in Technology
Modern technologies, such as time tracking software and project management platforms, offer features like automated task assignments, real-time progress tracking, and performance analytics.
These tools empower businesses to optimize work processes, identify bottlenecks, and allocate resources more efficiently.
By investing in time tracking apps, employers can gain a comprehensive understanding of work patterns, identify areas for improvement, and implement data-driven strategies to minimize the need for overtime.
Additionally, integrating technology fosters a collaborative and agile work environment, contributing to productivity gains.
7. Regular Training and Development
By investing in continuous employee training, organizations equip their workforce with the necessary skills and knowledge to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and optimize processes.
Well-trained employees are more adept at handling tasks, increasing productivity during regular working hours.
This proficiency diminishes the need for overtime to compensate for inefficiencies or mistakes.
Moreover, ongoing development initiatives foster a culture of improvement and innovation, creating a workforce that is not only skilled but also adaptable to evolving challenges.
Training programs can cover various aspects, including technology proficiency, time management, and project-specific skills.
Through these initiatives, companies cultivate a skilled and motivated workforce, reducing reliance on overtime.
This strategic approach not only controls costs but also contributes to the overall growth and competitiveness of the organization.

![Employee Time Clock Software and Fingerprint Scanner: 9 Options to Eliminate Time Theft & Buddy Punching [In-Depth Post]](https://buddypunch.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/employee-time-clock-software-and-fingerprint-scanner-768x461.png)